Rotomolded products are seamless, uniform in wall thickness and of single construction, which eliminates costly fabrication processes and the need for replacement parts. Rotomolded products include safety cones, plastic tanks, footballs, helmets, kayaks, playground slides, pipe fittings and outdoor planters. Read More…
As a full-service rotational molding company, Roto Dynamics is your source for high quality, custom rotomolded products. Since our inception, we have continued to earn success by closely working with our customers, developing innovative and tailored solutions. We are with you every step of the way, from design and development to production and assembly. For a complete view of our capabilities and ...

We are a custom manufacturer of rotationally molded products. Our state of the art technology creates precise, cost effective and dependable products. Whether your order is large or small, we want to be sure you are satisfied.
Western Industries Plastic Products, LLC, specializes in large-part plastic blow molding. We provide expertise and services in product design, process improvement, and product assemblies. We offer our customers comprehensive services and turnkey opportunities to achieve their specific project goals. We can assist with: R&D, product design, product improvement, and secondary-fixture design. For...
At Hi-Rel Plastics & Molding, we specialize in delivering high-performance solutions through advanced rotational molding. As a team deeply committed to precision and innovation, we bring decades of experience to the design and manufacture of custom rotationally molded products.

United States Plastic Corp. manufactures and distributes some 25,000 plastic items serving over 85,000 clients operating in a factory five acres under roof. Our major product is manufacturing plastic tanks, the distribution of bottles, carboy and plastic containers. This also includes plastic sheet, rods, tubes, flexible tubing and thousands of plastic fittings.

More Rotomoulding Companies
Rotomoulding: The Ultimate Guide to Rotational Moulding Materials, Process, and Applications
Rotomoulding, also known as rotational moulding or rotational molding, is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing process used to produce hollow plastic products. While polyethylene is the most commonly used thermoplastic material in rotomoulding, other plastics such as polypropylene, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), nylon (polyamide), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are also used to meet specific application requirements.
Looking to compare rotomoulding with other plastic moulding processes? Interested in the advantages and limitations of rotational moulding for your project? Explore below to discover how rotomoulding works, the top materials used, its diverse industrial applications, and the key benefits that make it the ideal choice for many manufacturers.
What Is Rotomoulding? Understanding the Rotational Moulding Process
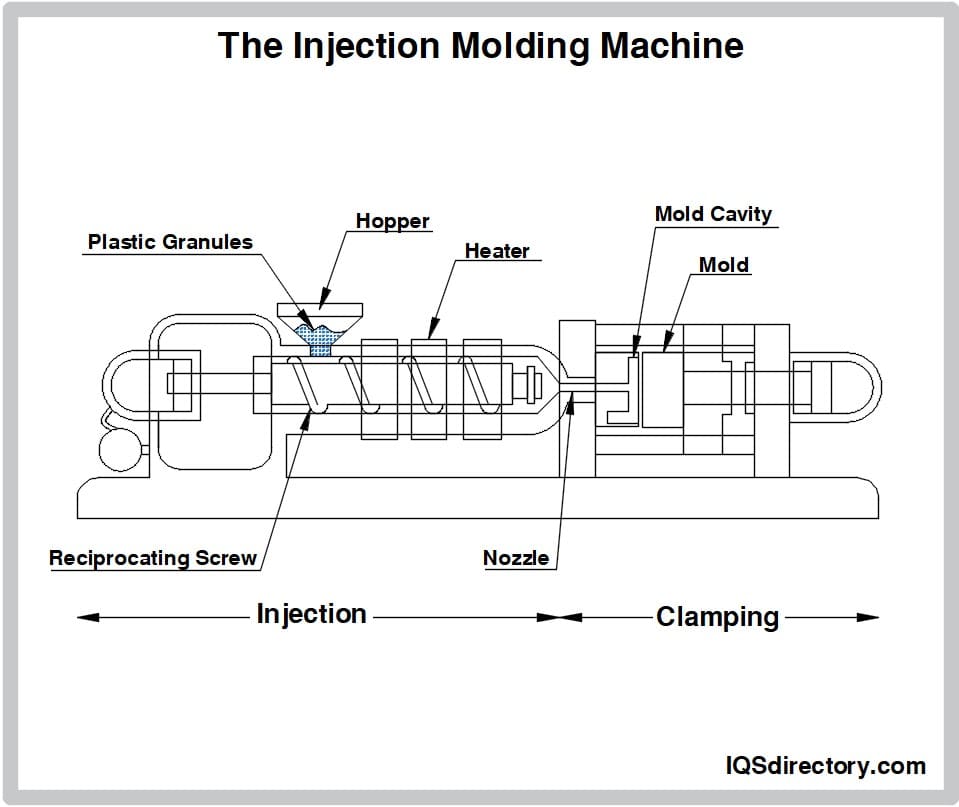
Rotomoulding is an alternative to manufacturing processes such as blow molding, injection molding, and thermoforming. While not as ubiquitous as these methods due to the need for large, specialized machinery, rotational moulding offers unique advantages for producing seamless, hollow, and highly durable plastic parts.
The rotomoulding process consists of several distinct steps:
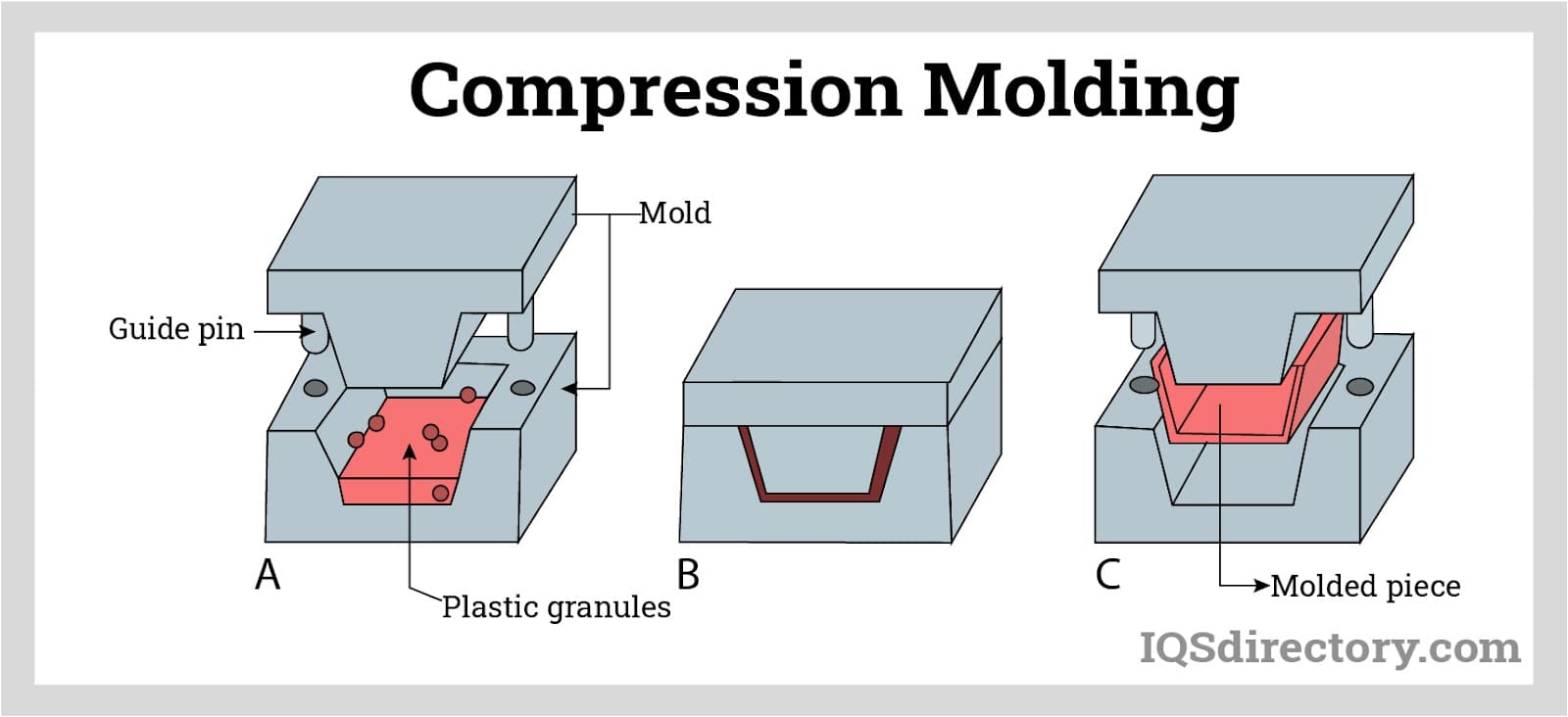
- Mold Fabrication: The process starts by fabricating a mold, which can be achieved through welding for simpler shapes, or die casting for more complex, precision-engineered designs. Molds are typically made from stainless steel, aluminum, or a combination of both, especially when uniform wall thickness is not required.
- Loading the Resin: A fine polymer resin powder—often linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) or high-density polyethylene (HDPE)—is measured and loaded into the mold. The powder must be extremely fine to ensure complete and even coverage of the mold’s internal surfaces. Additives can be mixed in to improve performance characteristics such as UV resistance, flame retardancy, chemical resistance, or to achieve specific colors, textures, and finishes.
- Heating and Rotating: The loaded mold is then mounted on a rotomoulding machine’s rotating spindle. The spindle rotates the mold on one or two axes as it is transported into a high-temperature oven. Here, the resin powder melts and coats the internal surfaces of the mold uniformly, forming a seamless hollow shape.
- Cooling: After thorough heating, the mold is moved into a cooling chamber, where a combination of cold air and water is used to solidify and cure the plastic. This step usually takes about 20 minutes, but may vary based on part size and material type.
- Demolding and Finishing: Once fully cooled, the mold is opened and the finished plastic part is manually removed. At this stage, rotomoulded products are typically hollow and have no openings or holes—these are cut out if needed. Additional post-processing steps such as cleaning, polishing, painting, or welding with small components are performed as required.
Key Materials Used in Rotomoulding
The selection of material is crucial in rotational moulding, as it directly affects product durability, performance, and suitability for specific environments. Here are the most common rotomoulding plastics and their core properties:
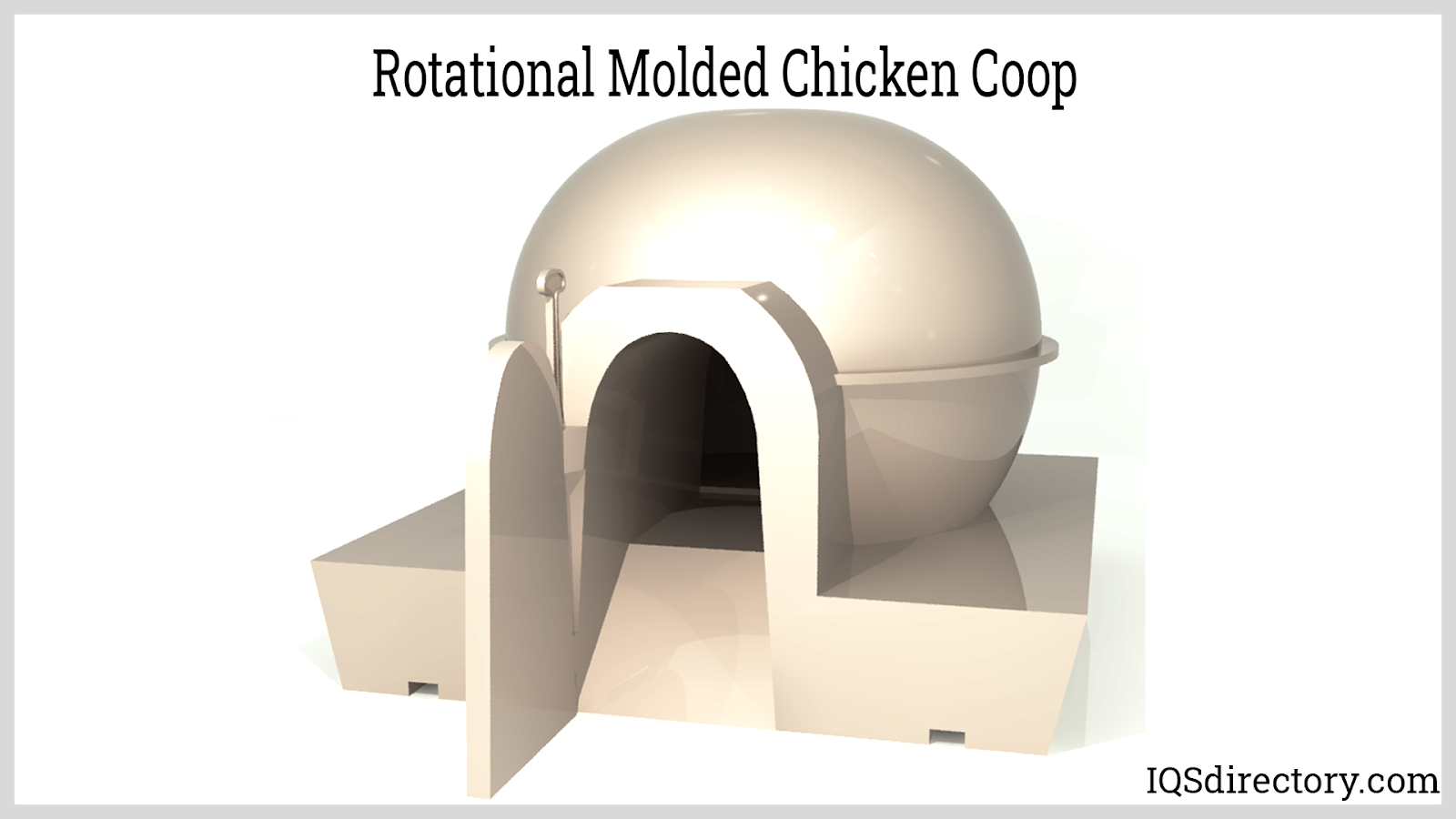
- Polyethylene (PE): The workhorse of rotational moulding, available in several grades including LDPE, LLDPE, and HDPE. Polyethylene is known for its excellent impact resistance, flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It is ideal for applications like tanks, bins, toys, and playground equipment.
- Polypropylene (PP): Offers improved stiffness and heat resistance compared to PE, making it suitable for parts exposed to higher temperatures or requiring enhanced rigidity, such as automotive components or industrial containers.
- Nylon (Polyamide, PA): Renowned for its strength, wear resistance, and ability to withstand elevated temperatures. Commonly used in technical applications demanding superior mechanical performance.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Valued for its flame retardancy and chemical stability, PVC is chosen for specialized applications such as medical devices, piping, and protective covers.
- Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF): A high-performance fluoropolymer that provides exceptional chemical resistance, UV resistance, and thermal stability. Used in demanding environments like chemical processing or outdoor infrastructure.
Additional additives and compounds can be incorporated into these base resins to enhance specific properties, including:
- UV Stabilizers – For outdoor durability and colorfastness
- Antimicrobial agents – For hygienic applications in food, beverage, and medical products
- Colorants and pigments – To achieve brand-specific colors or product differentiation
- Flame retardants – For increased safety in industrial or residential environments
- Foaming agents – To create lightweight, insulated structures
Rotomoulding vs. Other Plastic Moulding Methods
Trying to decide between rotomoulding and other plastics manufacturing techniques? Understanding the differences can help you select the best solution for your needs. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Moulding Process | Strengths | Limitations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotomoulding | Creates seamless, hollow, stress-free parts; cost-effective for large, low-volume products; easy color and material changes; complex shapes possible | Longer cycle times; less suitable for high-volume production; limited material selection | Tanks, containers, playground equipment, custom hollow parts |
| Injection Molding | High production speed; excellent surface finish; tight tolerances; suitable for high-volume manufacturing | Higher tooling costs; less suited for large or hollow products | Consumer goods, automotive parts, electronics housings |
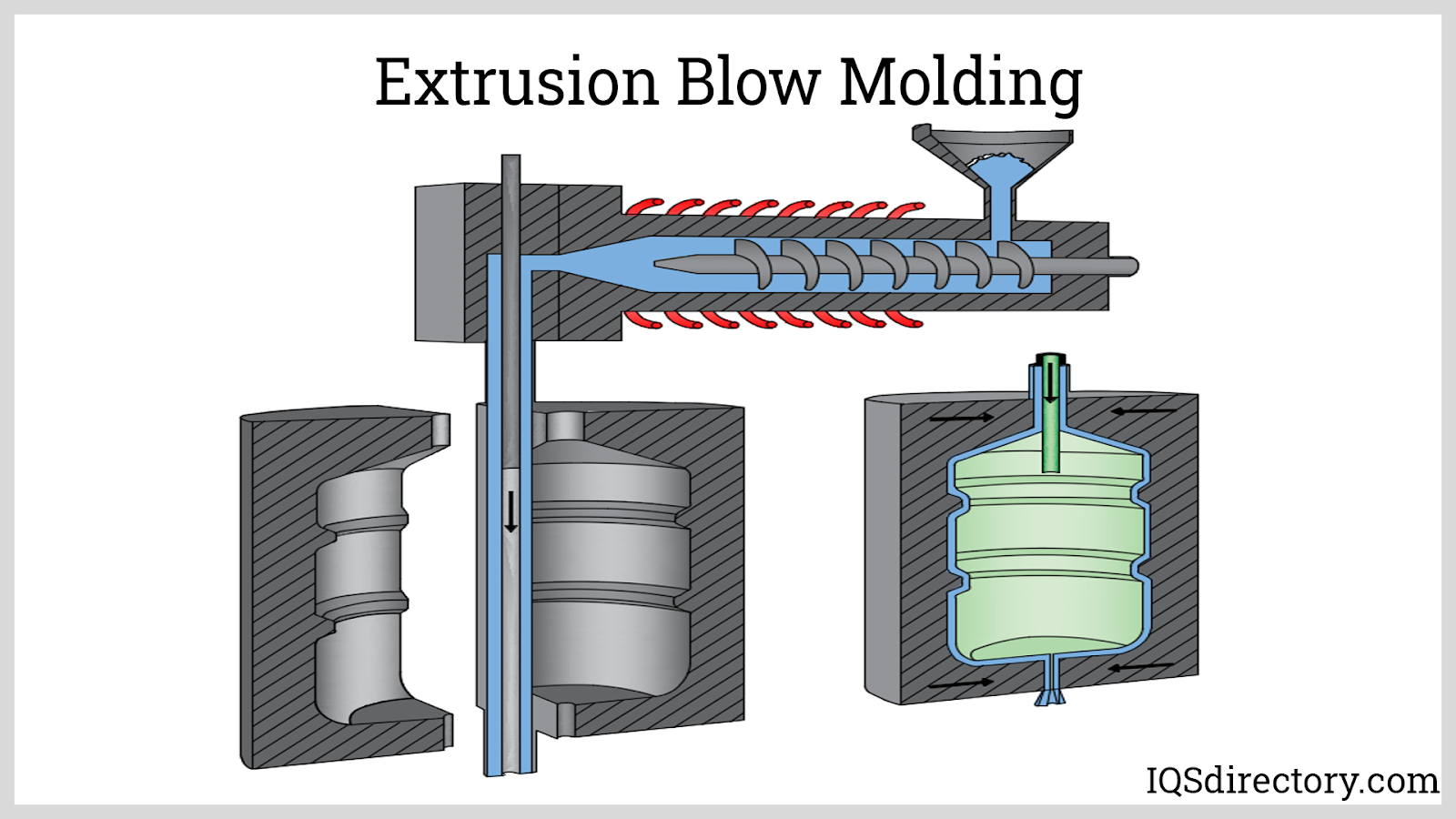
| Blow Molding | Efficient production of hollow parts; good for bottles and tanks; high output rates | Limited design complexity; not ideal for thick walls or intricate details | Bottles, drums, fuel tanks |
| Thermoforming | Low tooling cost; fast prototyping; suitable for large parts | Limited to sheet materials; less structural strength | Packaging, trays, enclosures |
Still unsure? Contact us to discuss your project needs and get expert advice on the best plastics manufacturing process for your application.
Industries and Use Cases for Rotomoulding
Rotomoulding is widely trusted across a diverse array of industries thanks to its flexibility, durability, and ability to produce large, seamless parts. Key sectors and use cases include:
- Water & Wastewater Management: Rotomoulded water tanks, chemical storage tanks, septic tanks, and dosing units benefit from seamless construction for leak-proof operation and chemical resistance.
- Marine Industry: Buoys, dock floats, boat components, and pontoons all require durability, UV stability, and resistance to saltwater and harsh weather.
- Agriculture: Feed bins, silos, fertilizer spreaders, and irrigation components where lightweight, corrosion-resistant structures are essential.
- Toy and Playground Equipment: Rotomoulded parts are impact-resistant, colorful, and safe for children, making them ideal for outdoor play equipment and large toys.
- Automotive & Transportation: Fuel tanks, air ducts, storage boxes, and tool cases designed for strength, reliability, and design flexibility.
- Pharmaceutical & Medical: Clean, hygienic, and chemical-resistant solutions for medical containers, device housings, and bioprocess tanks.
- Food & Beverage Processing: Food-grade bins, ingredient hoppers, and liquid containers that meet strict hygiene and safety standards.
- Construction: Barriers, cones, septic tanks, and custom enclosures for on-site durability and rapid deployment.
- Packaging & Material Handling: Stackable bins, pallets, and reusable containers for cost-effective, long-term logistics solutions.
- Furniture: Outdoor seating, planters, and modular furniture elements for weather resistance and aesthetic flexibility.
Wondering whether rotomoulding is the right fit for your application? Request a consultation with our technical team to discuss your requirements and get samples or quotes.
Advantages of Rotomoulding
Why choose rotomoulding over other plastics manufacturing processes? Here are some of the top advantages that drive buyer decisions:
- Design Flexibility: Easily produce complex, organic-shaped, or multi-walled structures with uniform wall thickness.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower tooling costs compared to injection or blow molding, especially for short production runs or large parts.
- Seamless Construction: No weld lines or joints, reducing weak points and potential for leaks—critical for tanks and containers.
- Material & Color Versatility: Easily switch between materials or colors without extensive downtime or cleaning.
- Stress-Free Parts: The low-pressure process minimizes residual stresses and warping, enhancing durability.
- Superior Impact & Chemical Resistance: Rotomoulded products withstand harsh environments, making them ideal for outdoor, marine, and industrial use.
- Hollow, Lightweight Products: Achieve high strength-to-weight ratios and buoyancy for applications like floats and pontoons.
- Customization: Add logos, textures, or functional inserts directly into the mold for unique branding or performance features.
Limitations and Considerations in Rotomoulding
While rotomoulding offers many benefits, it’s important to understand its limitations and key decision factors before selecting this process:
- Longer Cycle Times: Rotational moulding typically has slower production cycles compared to injection or blow molding.
- Limited Material Choices: Not all thermoplastics are suitable for the process; best results are achieved with PE, PP, nylon, PVC, and PVDF.
- Lower Dimensional Precision: Tolerances are usually broader, making the process less suitable for parts with intricate or tight-fitting components.
- Manual Demolding: Parts are removed by hand, which can increase labor costs for high-volume production.
- Wall Thickness Variability: While uniformity is achievable, extremely thick or thin sections can be challenging without careful design and process control.
Need help evaluating if rotomoulding is right for your next product? Contact our engineering team for a free design review or prototyping consultation.
How to Choose a Rotomoulding Partner: What to Look For
Choosing the right rotomoulding manufacturer can make all the difference in your product’s performance, cost, and time-to-market. Here’s what to consider when researching rotational moulding suppliers:
- Experience & Technical Expertise: Look for a proven track record with similar products and industries.
- Material Selection: Ensure the supplier offers a wide range of certified rotational moulding resins and can advise on the best material for your needs.
- Design Support: The best partners offer in-house engineering to optimize product design for manufacturability and performance.
- Quality Assurance: Check for ISO certification, documented quality control processes, and a history of meeting industry standards.
- Production Capacity: Can they handle your required volume? Do they offer rapid prototyping or short-run manufacturing?
- Customization & Value-Added Services: From color matching and branding to assembly and logistics, value-added options can streamline your supply chain.
- Customer References: Ask for case studies, testimonials, or references from similar projects.
Ready to request a quote or schedule a plant tour? Contact our sales team to start your rotomoulding project today.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rotomoulding
- What is the minimum order quantity for rotomoulded products?
MOQ depends on product size, complexity, and supplier capabilities. Many manufacturers offer flexibility for prototyping and small production runs. - Can rotomoulded products be recycled?
Yes, most rotomoulded plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene are fully recyclable. Ask your supplier about sustainable material options. - What is the typical lead time for custom rotomoulded parts?
Lead times vary but are usually 4–8 weeks from design approval, depending on mold complexity and order volume. - How are customized colors or textures achieved in rotomoulding?
Colorants and texture plates are added during the molding process, allowing for endless aesthetic options. - Are rotomoulded products suitable for food contact or medical use?
Yes, with the right resins and additives, rotomoulded parts can meet FDA, EU, and other regulatory standards for food and medical applications. - How do I choose between rotomoulding and injection molding?
Consider product size, hollow structure needs, production volume, cost, and required tolerances. Rotomoulding excels for large, hollow, or low-volume parts.
Didn’t find your answer? Visit our full FAQ for expert help.
Get Started with Rotomoulding: Next Steps
Whether you’re developing a new product or optimizing an existing design, rotational moulding offers a unique set of advantages for producing durable, custom, and cost-effective plastic parts. From industrial tanks and marine floats to playground equipment and food-grade containers, rotomoulding delivers unmatched flexibility and value.
Explore more about rotomoulding materials, applications, and benefits throughout our website.





 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators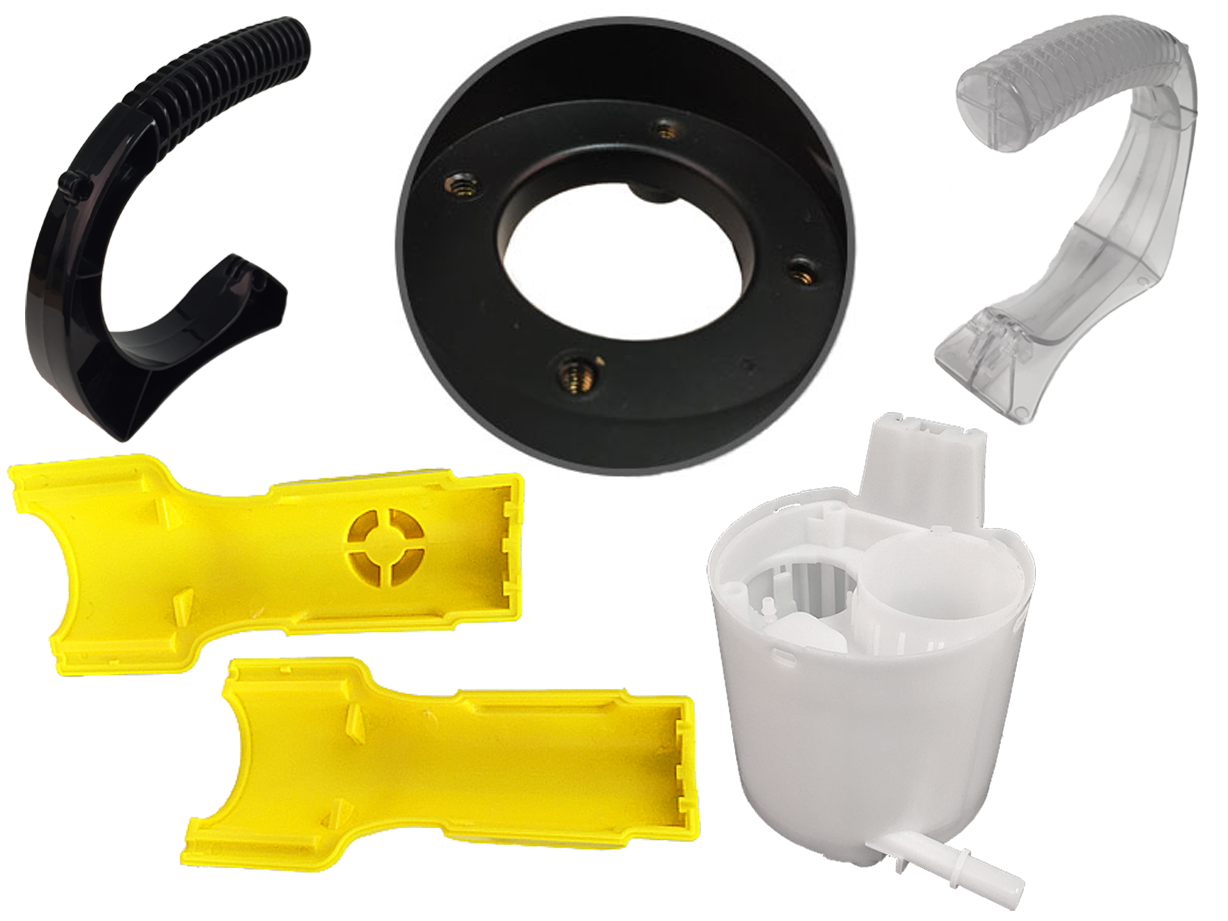 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics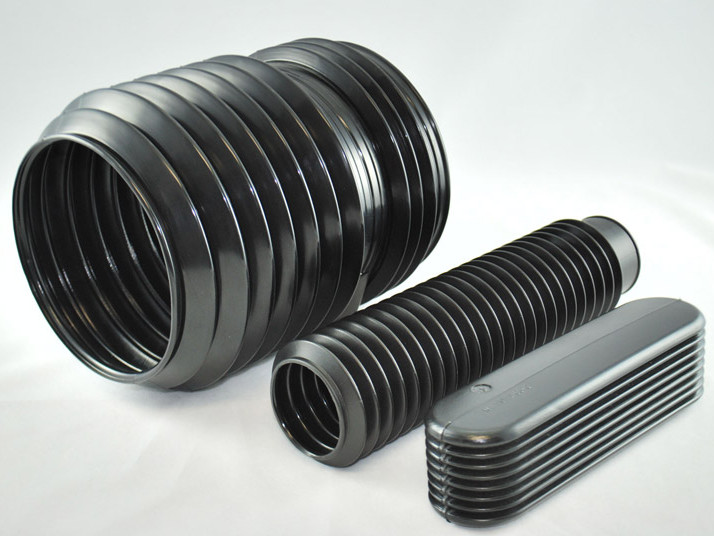 Plastic Blow Molding
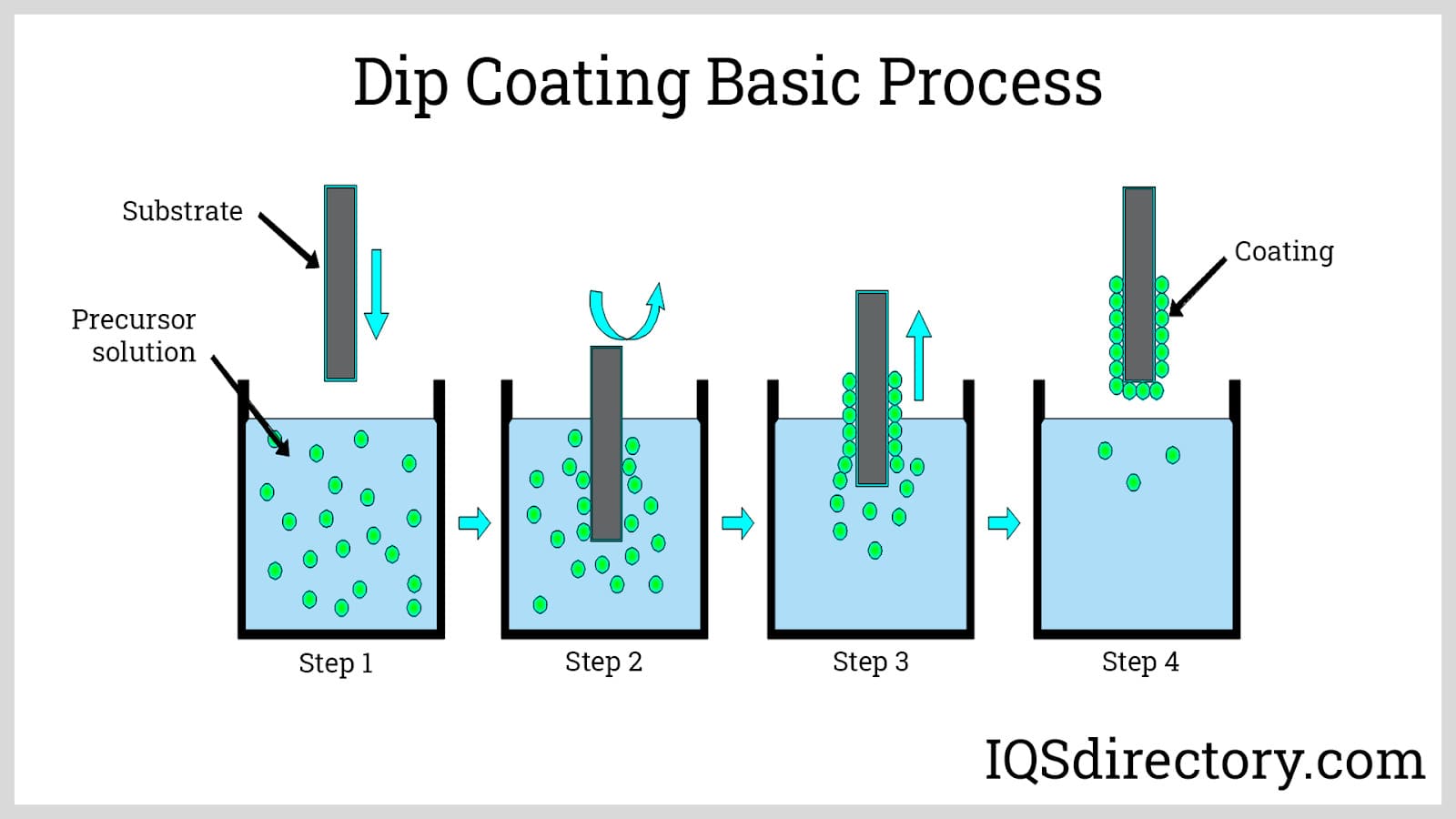
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding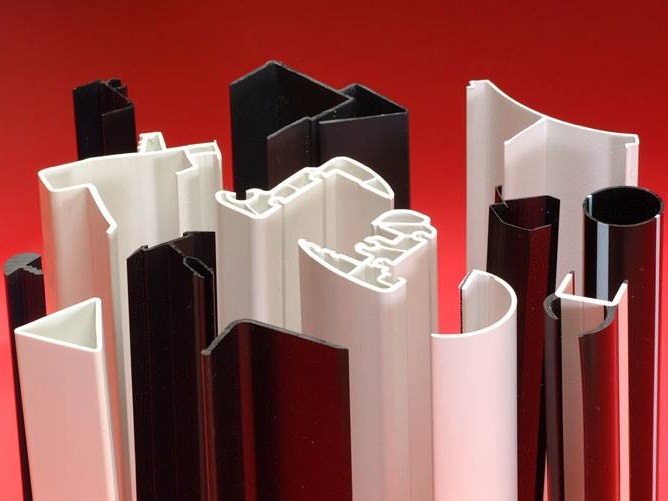 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding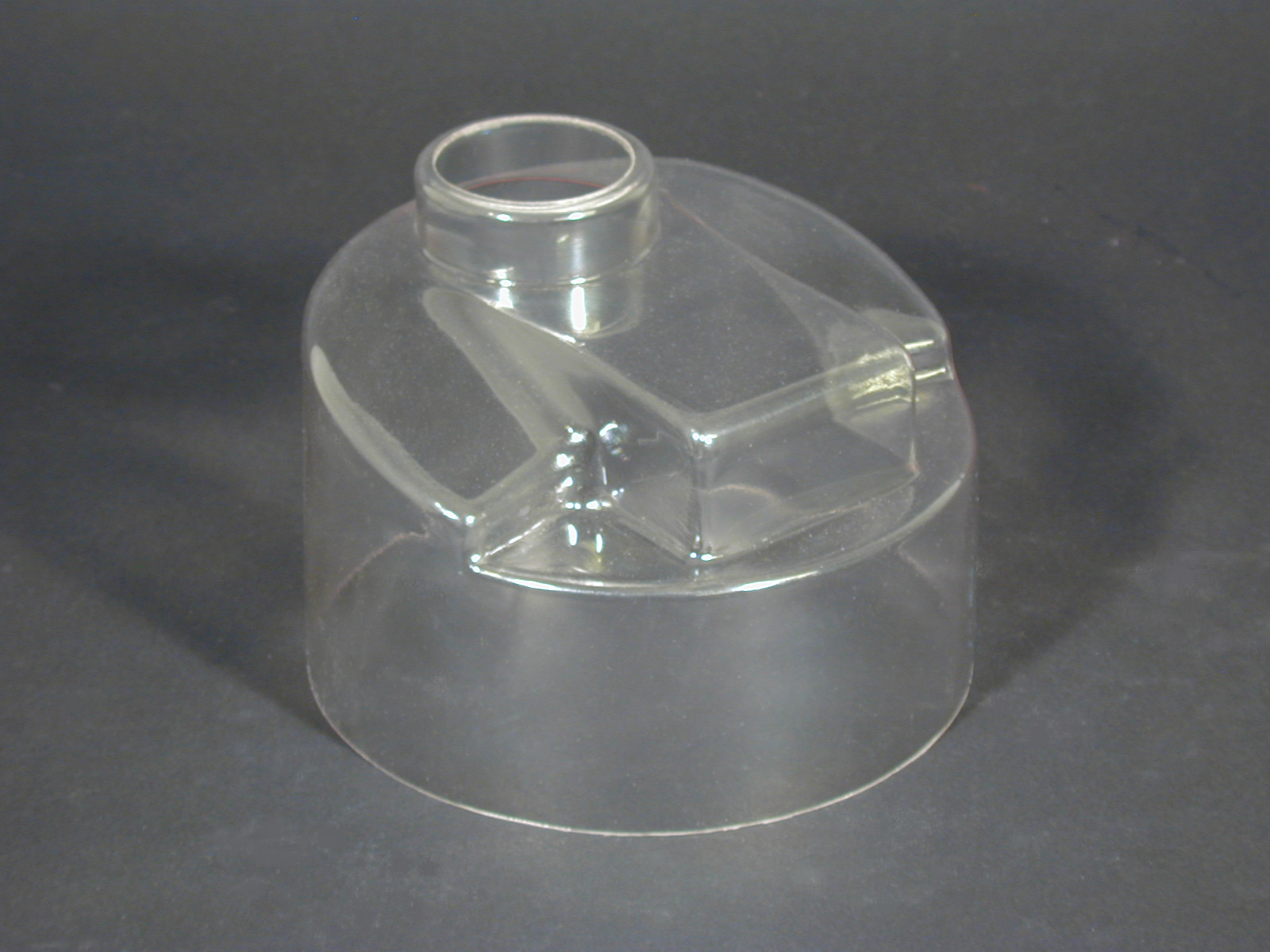 Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services