Rotational molding, sometimes referred to as rotomolding, rotomolded, or roto-casting, is an industrial technique for producing hollow parts of any size. The best options for rotational molding are large, single-piece hollow components and double-walled open containers. This is an economical way to make big plastic pieces. A heated, gently rotating mold is filled with resin and rotated vertically and horizontally. Simultaneously heating and rotating, the resin is dispersed and fused on the inside surfaces of the mold. Read More…
As a full-service rotational molding company, Roto Dynamics is your source for high quality, custom rotomolded products. Since our inception, we have continued to earn success by closely working with our customers, developing innovative and tailored solutions. We are with you every step of the way, from design and development to production and assembly. For a complete view of our capabilities and ...

We are a custom manufacturer of rotationally molded products. Our state of the art technology creates precise, cost effective and dependable products. Whether your order is large or small, we want to be sure you are satisfied.
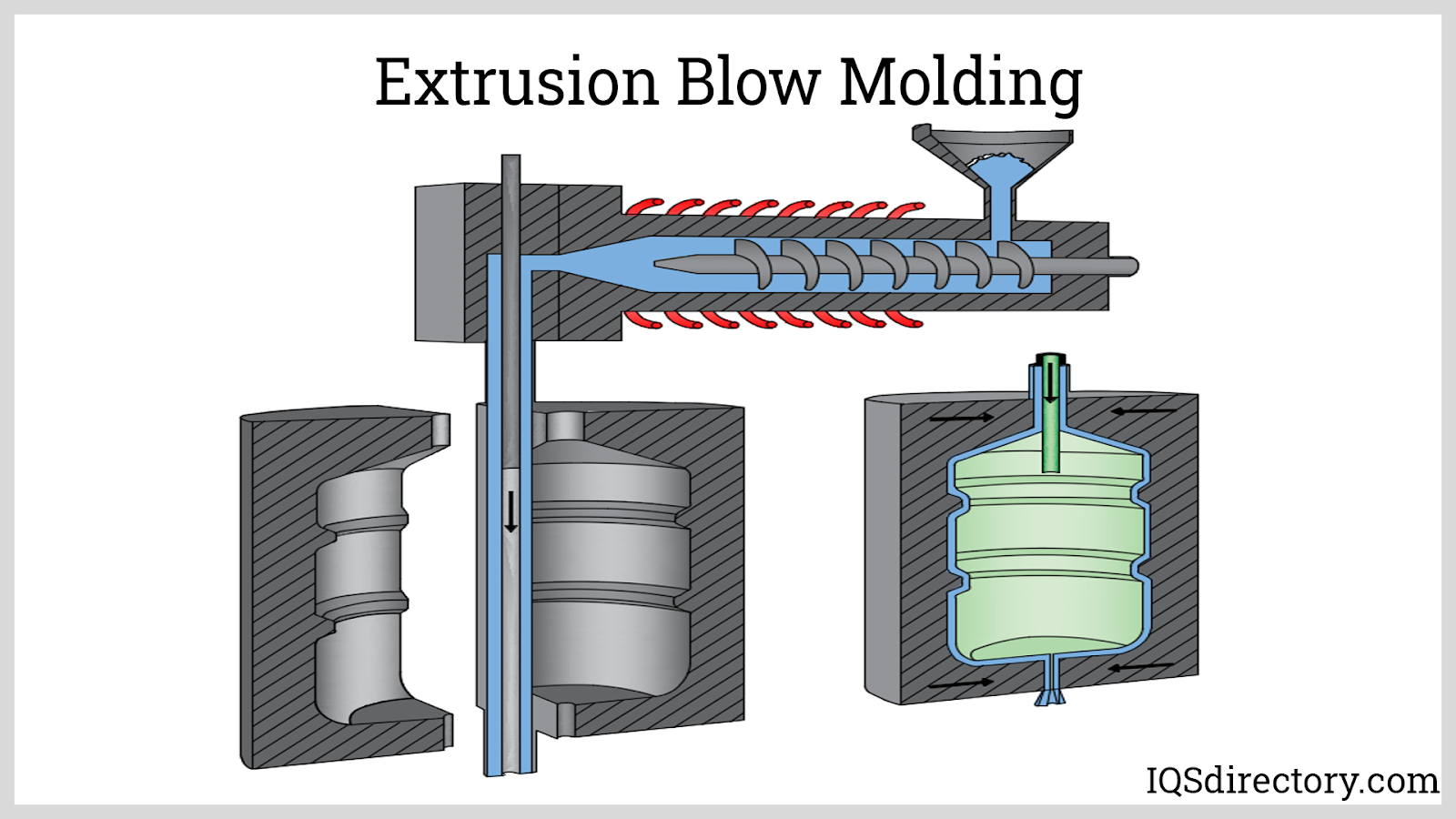
Western Industries Plastic Products, LLC, specializes in large-part plastic blow molding. We provide expertise and services in product design, process improvement, and product assemblies. We offer our customers comprehensive services and turnkey opportunities to achieve their specific project goals. We can assist with: R&D, product design, product improvement, and secondary-fixture design. For...
At Hi-Rel Plastics & Molding, we specialize in delivering high-performance solutions through advanced rotational molding. As a team deeply committed to precision and innovation, we bring decades of experience to the design and manufacture of custom rotationally molded products.

United States Plastic Corp. manufactures and distributes some 25,000 plastic items serving over 85,000 clients operating in a factory five acres under roof. Our major product is manufacturing plastic tanks, the distribution of bottles, carboy and plastic containers. This also includes plastic sheet, rods, tubes, flexible tubing and thousands of plastic fittings.

More Rotomolding Companies

Rotomolding Process: An In-Depth Guide to Rotational Molding
Rotational molding, also known as rotomolding, is a highly versatile plastic molding process used to manufacture hollow, seamless, and durable objects of all shapes and sizes. The process begins by loading a preweighted amount of polymer, often in powder or liquid form, into one half of a mold, which is typically constructed from aluminum or steel for optimal thermal conductivity and long life. This mold is then sealed and placed into an oven, where it undergoes biaxial rotation—rotating on two perpendicular axes simultaneously—at speeds generally ranging from 2 to 20 rpm. The rotation ensures even distribution of the polymer along the internal surfaces of the mold.
As the mold heats, the polymer melts (or reacts, in the case of thermoset resins), gradually coating the mold’s interior. The careful thermal management and slow rotation characteristic of the rotomolding process allow gravity and heat to work together, forming uniform wall thickness and minimizing stress within the finished product. Once the polymer has coated the entire surface and the pool of raw material disappears, the mold is transferred to a cooling chamber. Here, it undergoes controlled cooling—often aided by fans or water mist—to solidify the part and prevent warping. Once cooled, the mold is opened and the finished product is ejected, ready for post-processing or immediate use. This cycle can then be repeated for consistent, high-quality results.
Key Steps in Rotomolding Manufacturing:
- Loading polymer resin (usually polyethylene or other thermoplastics) into the mold
- Sealing and rotating the mold within a heating chamber
- Melting and even distribution of resin by biaxial rotation
- Controlled cooling to solidify the molded part
- Demolding and post-processing such as trimming or assembly
Are you curious about how rotational molding compares to other plastic manufacturing techniques like injection molding or blow molding? Learn more about the differences and best use cases for each process.
Rotomolding Products: Applications, Use Cases, and Industry Solutions
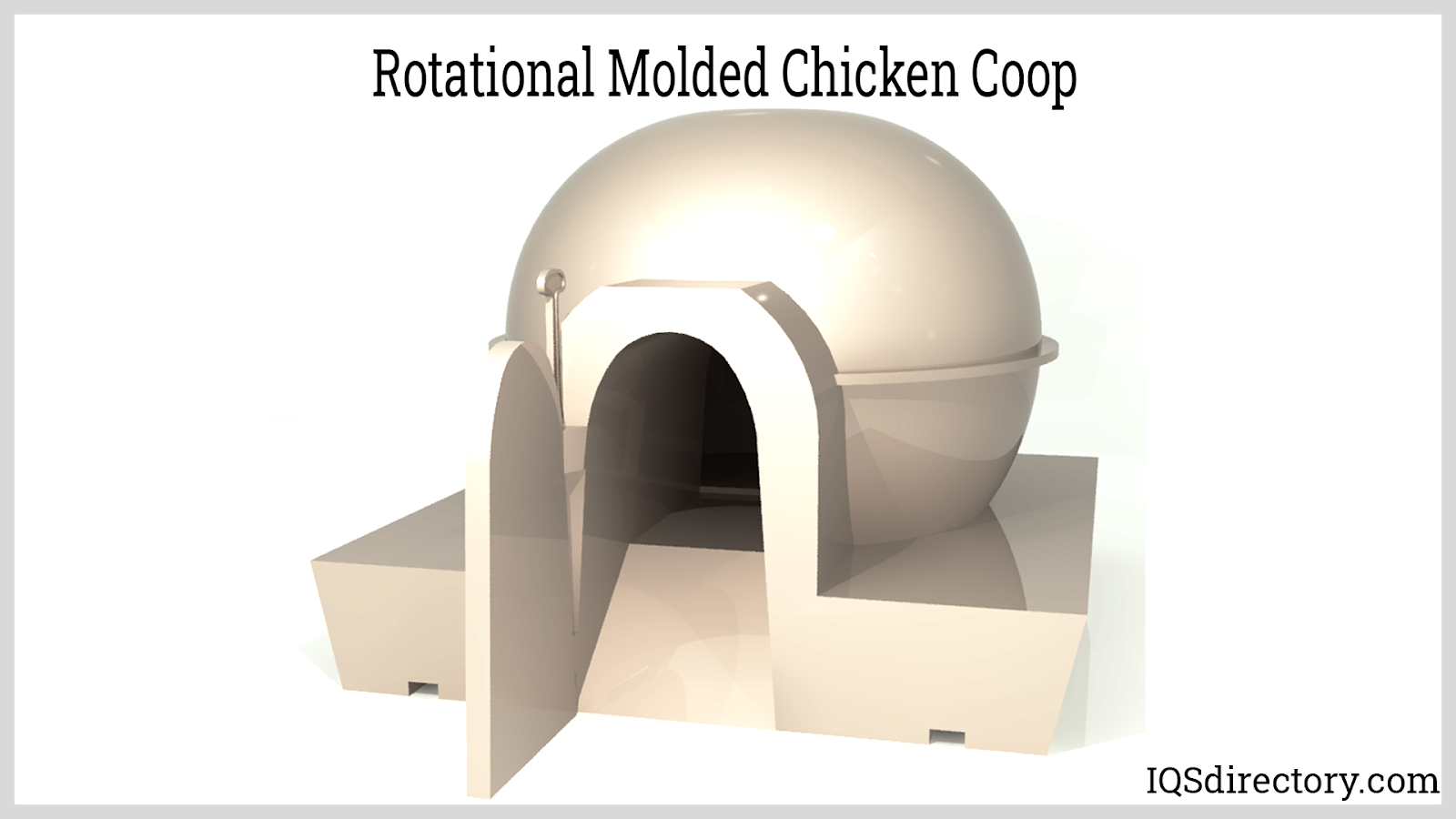
The industrial and commercial applications for products made using rotational molding are virtually limitless. Rotomolded plastic parts are renowned for their durability, chemical resistance, and seamless construction, making them the preferred solution in industries ranging from agriculture and construction to medical, automotive, and recreational sectors. Manufacturers are increasingly choosing rotomolding to convert products previously made from metal, fiberglass, or less resilient plastics due to its cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and superior product performance.
Common examples of rotomolded products include:
- Industrial storage tanks: chemical tanks, water tanks, septic tanks, and fuel containment units
- Pallets and containers: reusable shipping pallets, bulk bins, and air cargo containers
- Agricultural equipment: feed and fertilizer hoppers, pesticide sprayers, and irrigation components
- Commercial carts: laundry carts, housekeeping trolleys, and material handling bins
- Piping systems: drainage pipes, sewer pipes, and underground conduits
- Safety and shelter products: tornado shelters, emergency safety cabinets, and burial urns
- Outdoor and recreational items: playground equipment, kayaks, canoes, and coolers
- Military and defense articles: ruggedized cases, equipment housings, and sensitive electronics enclosures
- Medical equipment: hygienic storage units, sterilization trays, and biohazard waste containers
- Custom OEM parts: automotive components, appliance housings, and point-of-purchase displays
Looking for specific examples or custom solutions for your project? Contact us to discuss your rotomolding needs and get expert advice on the best materials and design options.

Types of Rotomolding Machines: Selecting the Right Equipment for Your Application
The rotational molding process utilizes several types of machinery, each with unique features and benefits for different production volumes, part geometries, and operational requirements. Choosing the right rotomolding machine is crucial for optimizing efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring high-quality production outcomes.
- Rock and roll machine: Specializes in producing long, narrow parts and cylindrical shapes. Ideal for tanks, pipes, and canoes.
- Clamshell producer: Compact footprint; both heating and cooling occur within the same chamber. Well-suited for small to medium production runs.
- Up and over rotational machine: Features vertical movement for efficient mold handling, often chosen for space-constrained facilities.
- Material jetting machine: Advanced technology for precise material deposition, used for complex or custom applications.
- Shuttle machine: Typically equipped with two independent arms that alternate between heating and cooling stations, maximizing throughput for medium to high-volume production.
- Swing arm machine: Offers up to four arms with biaxial movement, perfect for applications requiring extended cooling cycles or lengthy demolding times.
- Carousel machine: Designed for continuous, high-volume production. Multiple arms rotate molds through heating, cooling, and loading/unloading stations.
When evaluating rotomolding equipment, consider factors such as part size, cycle time, production volume, plant layout, energy efficiency, and automation capabilities to ensure your investment aligns with your operational goals.

Industries and Applications: Where Is Rotomolding Used?
Rotational molding technology is widely adopted across diverse industries due to its ability to create robust, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant parts. Explore some of the most common sectors benefiting from rotomolding solutions:
Food and Beverage Sector
Rotomolded insulated containers and packaging are ideal for transporting and storing temperature-sensitive food products, dry ice, and perishable goods. FDA-approved polyethylene and foam-insulated rotomolded containers ensure compliance with food safety regulations and provide superior thermal performance. Applications include seafood transport, wine fermentation tanks, and bulk ingredient storage.
Military and Defense Sector
The military and defense industries require rugged, impact-resistant cases and packaging to safeguard sensitive equipment during transport and deployment. Rotomolded military cases, toolboxes, and storage containers offer exceptional strength, watertight integrity, and the ability to withstand harsh environments, making them a trusted choice for defense logistics and field operations.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Sector
Medical device manufacturers rely on rotomolded solutions for sterile storage, safe transport, and ergonomic handling of delicate instruments and pharmaceuticals. Custom-designed rotomolded cases meet stringent hygiene and regulatory standards, supporting healthcare providers in delivering safe and efficient patient care.
Agricultural and Environmental Applications
Farmers and environmental engineers utilize rotomolded tanks, bins, and composters for water storage, chemical mixing, irrigation, and waste management. The chemical resistance and UV stability of rotomolded polyethylene components ensure long service life in demanding outdoor settings.
Transportation and Logistics
Rotomolded pallets, reusable containers, and bulk bins are favored in supply chain management due to their durability, stackability, and resistance to impact and moisture. Their seamless construction helps prevent contamination and facilitates easy cleaning, critical in food, pharmaceutical, and high-purity environments.
Recreational, Marine, and Outdoor Products
Rotomolding is indispensable for manufacturing kayaks, canoes, playground equipment, coolers, and outdoor furniture. The process’s ability to create complex shapes, vibrant colors, and seamless finishes ensures both aesthetic appeal and long-term performance in recreational goods.
Still have questions about rotomolding applications in your industry? Ask us how rotomolding can solve your specific business challenges.
Advantages of Rotomolding: Why Choose Rotational Molding for Your Plastic Products?
- Uniform wall thickness: Biaxial rotation and slow heating produce consistent wall thickness, which enhances mechanical properties and product reliability.
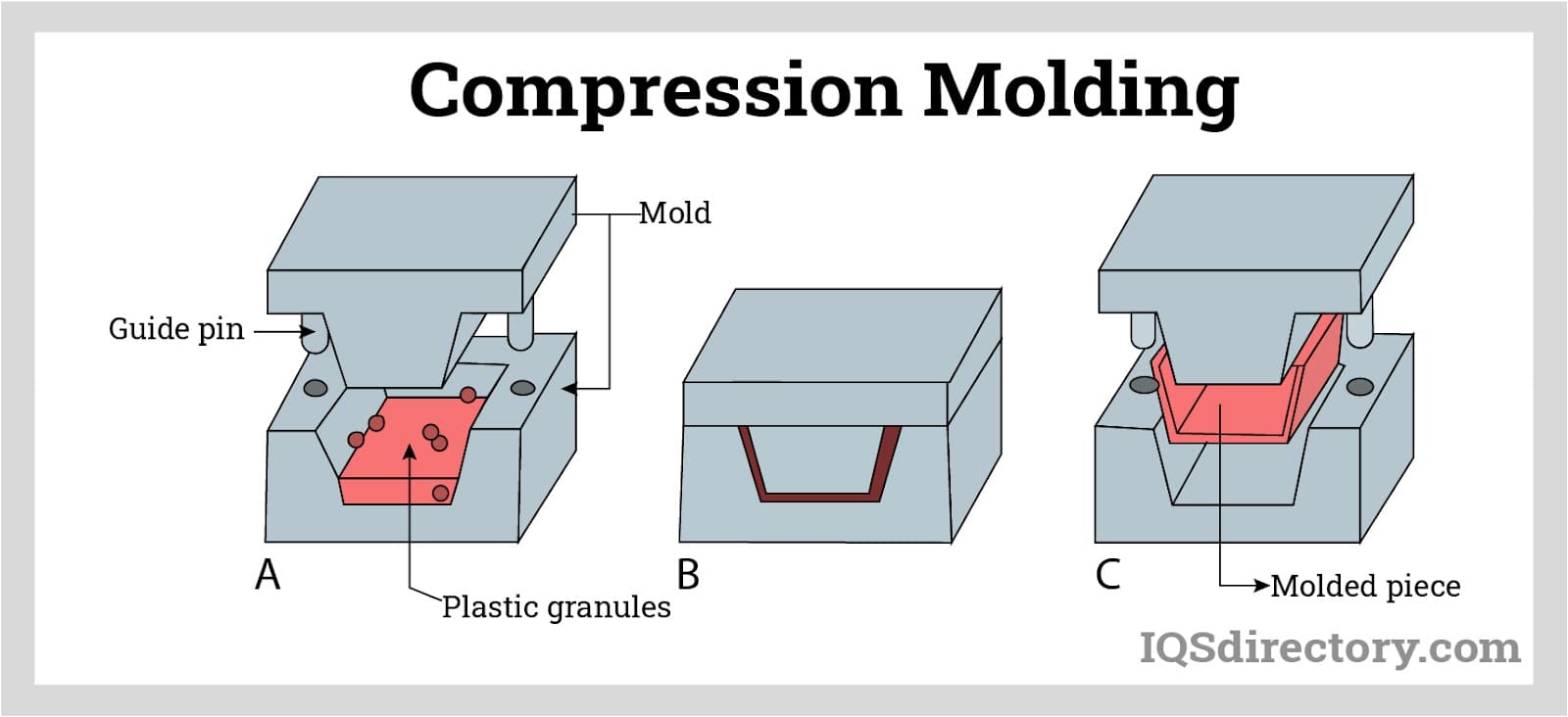
- Low tooling and mold costs: Compared to injection or blow molding, rotomolding requires simpler, less expensive molds, making it cost-effective for short to medium production runs and prototyping.
- Design flexibility: Rotomolding accommodates intricate geometries, undercuts, and integrated features such as threads, inserts, ribs, and multi-wall structures without the need for secondary assembly.
- Material selection: A variety of polymers—including polyethylene (HDPE, LLDPE), polypropylene, and specialty resins—can be used, allowing customization for chemical resistance, UV stability, and impact strength.
- Color and finish options: Additives and pigments can be blended with the resin for custom colors, textures, and branding, all in a single process step.
- Eco-friendly process: Minimal material waste, energy-efficient machinery, and the ability to recycle scrap resin contribute to sustainability and lower environmental impact.
- Stress-free parts: The absence of injection points and gradual cooling result in products with minimal internal stress, reducing the risk of cracking or deformation.
- One-piece construction: Complex assemblies can often be produced as a single part, eliminating the need for fasteners, adhesives, or welding, and reducing labor costs and potential failure points.
Are you weighing the benefits of rotomolding over other manufacturing methods? Compare rotomolding to injection, blow, and thermoforming to see which process is right for you.
Drawbacks of Rotomolding: Considerations and Limitations
- Slower production cycles: The heating and cooling stages are inherently time-consuming, making rotomolding less competitive for extremely high-volume, fast-turnaround production.
- Heavier products: Rotomolding often uses more polymer material than processes like blow molding, resulting in sturdier but heavier parts.
- Lower thermal efficiency: Conventional rotomolding ovens may consume more energy and require longer cycles, contributing to increased operational costs unless state-of-the-art equipment is used.
- Surface finish limitations: Achieving highly polished surface finishes can be challenging compared to injection molding.
- Material restrictions: Not all polymers are suitable for rotomolding; most commonly, polyethylene and select thermoplastics are used.
- Complexity in thin-walled parts: While rotomolding excels at producing uniform walls, extremely thin-walled or intricate internal structures may be more difficult to achieve.
Do you need help determining if rotomolding fits your application, or are you exploring alternative plastic manufacturing methods? Contact our experts for a tailored process comparison and guidance.
How to Choose the Best Rotomolding Company for Your Project
Finding the right rotomolding manufacturer or supplier is essential for product quality, project timelines, and overall success. Here are important decision factors to consider when evaluating rotomolding companies:
- Experience and reputation: Review the company's portfolio, years in business, and feedback from past clients. Look for expertise in your specific industry or product type.
- Capabilities and equipment: Ensure the company has the right machinery, material options, and technical know-how to handle your project’s complexity and scale.
- Quality assurance: Ask about certifications (ISO, FDA, etc.), inspection protocols, and quality control measures throughout the production process.
- Design and engineering support: A reputable rotomolding supplier should offer design assistance, prototyping, and value engineering to optimize cost and manufacturability.
- Customization and secondary services: Consider whether the manufacturer provides assembly, painting, labeling, or other finishing operations to deliver a turnkey product.
- Lead times and flexibility: Choose a partner who can meet your delivery schedule, accommodate design changes, and scale production as your business grows.
- Pricing and total cost of ownership: Request detailed quotes, understand what’s included, and compare value—not just price—when selecting a rotomolding partner.
To ensure the most productive outcome when selecting a rotomolding company, compare at least five providers using our comprehensive rotomolding directory. Each rotomolder’s business profile highlights their areas of expertise, capabilities, case studies, and a direct contact form for more information or a personalized quote. Use our patented website previewer to quickly evaluate what each manufacturer specializes in, then submit your project details using our streamlined RFQ form to reach multiple rotomolding companies at once. This approach maximizes your chances of finding the best fit for your needs and budget.
Ready to take the next step? Request a quote or schedule a design consultation with leading rotomolding manufacturers today.
Rotomolding vs. Other Plastic Manufacturing Processes: Which Is Best for You?
When selecting a plastic manufacturing process, it’s essential to consider your product’s intended use, design complexity, required volumes, and performance requirements. Here’s how rotational molding compares to other popular techniques:
- Rotomolding vs. Injection Molding: Injection molding excels at high-volume production of small, highly detailed parts but requires expensive tooling and is less suitable for large, hollow objects. Rotomolding offers lower tooling costs, seamless construction, and is ideal for robust, large, or hollow parts but at a slower cycle time.
- Rotomolding vs. Blow Molding: Blow molding is used primarily for hollow parts like bottles and tanks, but is limited in part geometry and wall thickness control. Rotomolding provides greater design flexibility, thicker walls, and the ability to incorporate complex features.
- Rotomolding vs. Thermoforming: Thermoforming shapes flat plastic sheets using heat and pressure, suitable for large, single-surface parts. Rotomolding, by contrast, creates fully enclosed, hollow objects with uniform walls and integrated features.
Not sure which process is right for your next project? Speak with a rotational molding specialist to get a tailored process recommendation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Rotomolding
What materials are commonly used in rotomolding?
The most widely used material in rotomolding is polyethylene (including HDPE and LLDPE), due to its excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and chemical stability. Other materials used include polypropylene, PVC, nylon, and specialty resins for specific performance characteristics such as flame retardancy or UV resistance. Looking for a food-safe or chemical-resistant resin? Contact us for recommendations based on your application.
How durable are rotomolded products?
Rotomolded products are highly durable, offering superior resistance to impact, corrosion, and environmental degradation. The seamless construction and even wall thickness make them ideal for demanding applications in agriculture, transportation, and outdoor environments.
Can rotomolding be used for custom or low-volume production?
Yes, rotomolding is especially cost-effective for prototypes, custom products, and small to medium production runs due to its low tooling costs and design flexibility. Custom colors, textures, and integrated features can be easily achieved without expensive retooling.
What are typical lead times for rotomolded parts?
Lead times vary based on part complexity, quantity, and post-processing requirements. Typical projects range from several weeks for initial prototyping to a few months for full-scale production. Need expedited manufacturing? Ask about our rapid prototyping and accelerated production options.
How do I get started with a rotomolding project?
Begin by outlining your product requirements: size, shape, material, color, quantity, and intended use. Then, consult with a reputable rotomolding manufacturer to discuss design optimization, material selection, and cost estimates. Submit your project details to receive a free consultation and quote.
Get Started: Request a Rotomolding Quote or Consultation
Whether you’re developing a new product, upgrading an existing design, or seeking to improve manufacturing efficiency, rotational molding offers unique advantages for high-quality plastic parts. Browse our directory of trusted rotomolding companies or request a quote today to connect with industry experts who can bring your vision to life.
Need more information? Explore our in-depth guides on rotomolding materials, design best practices, and latest industry trends to stay ahead in the world of plastic manufacturing.





 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators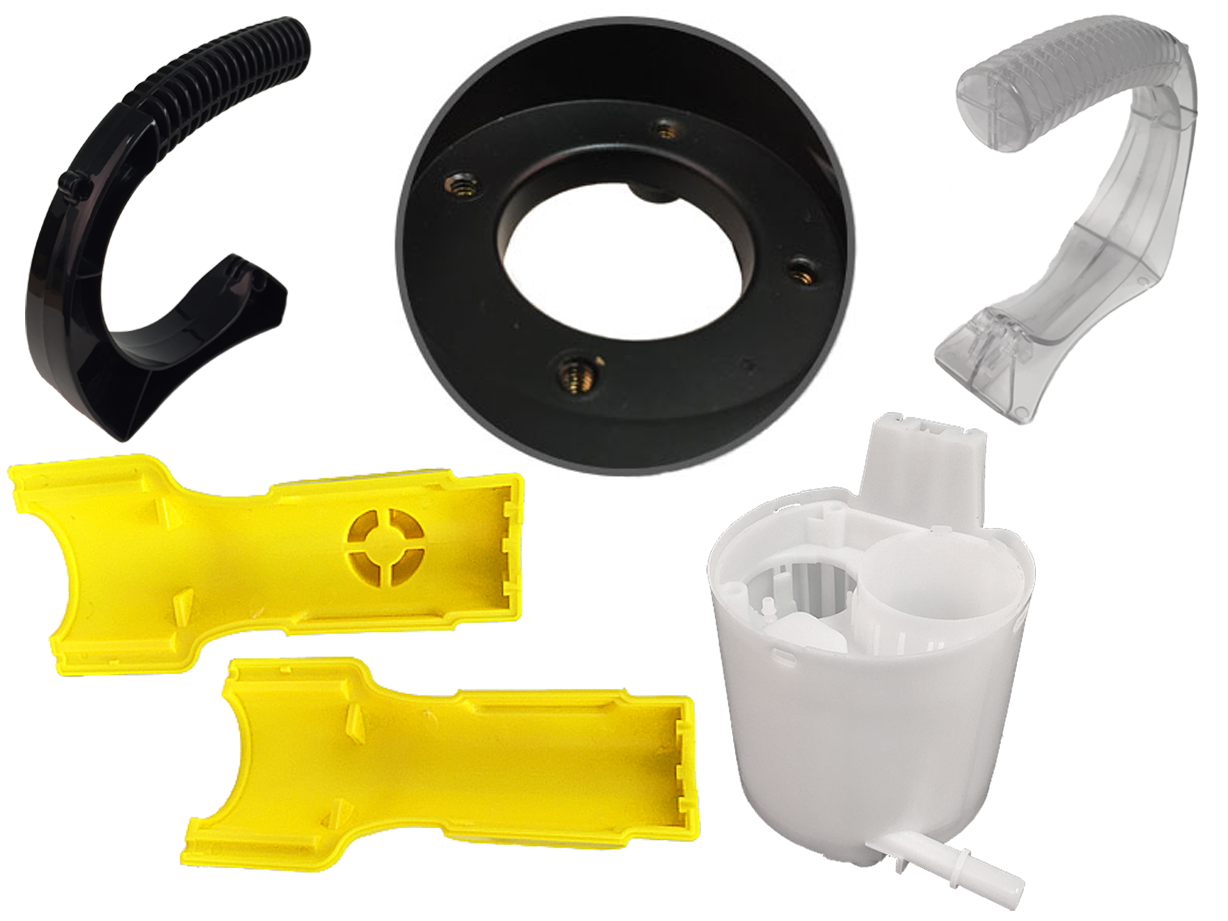 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics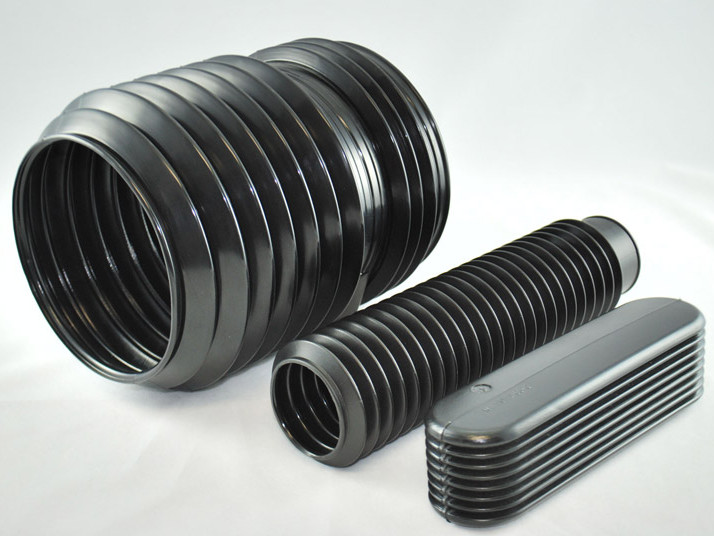 Plastic Blow Molding
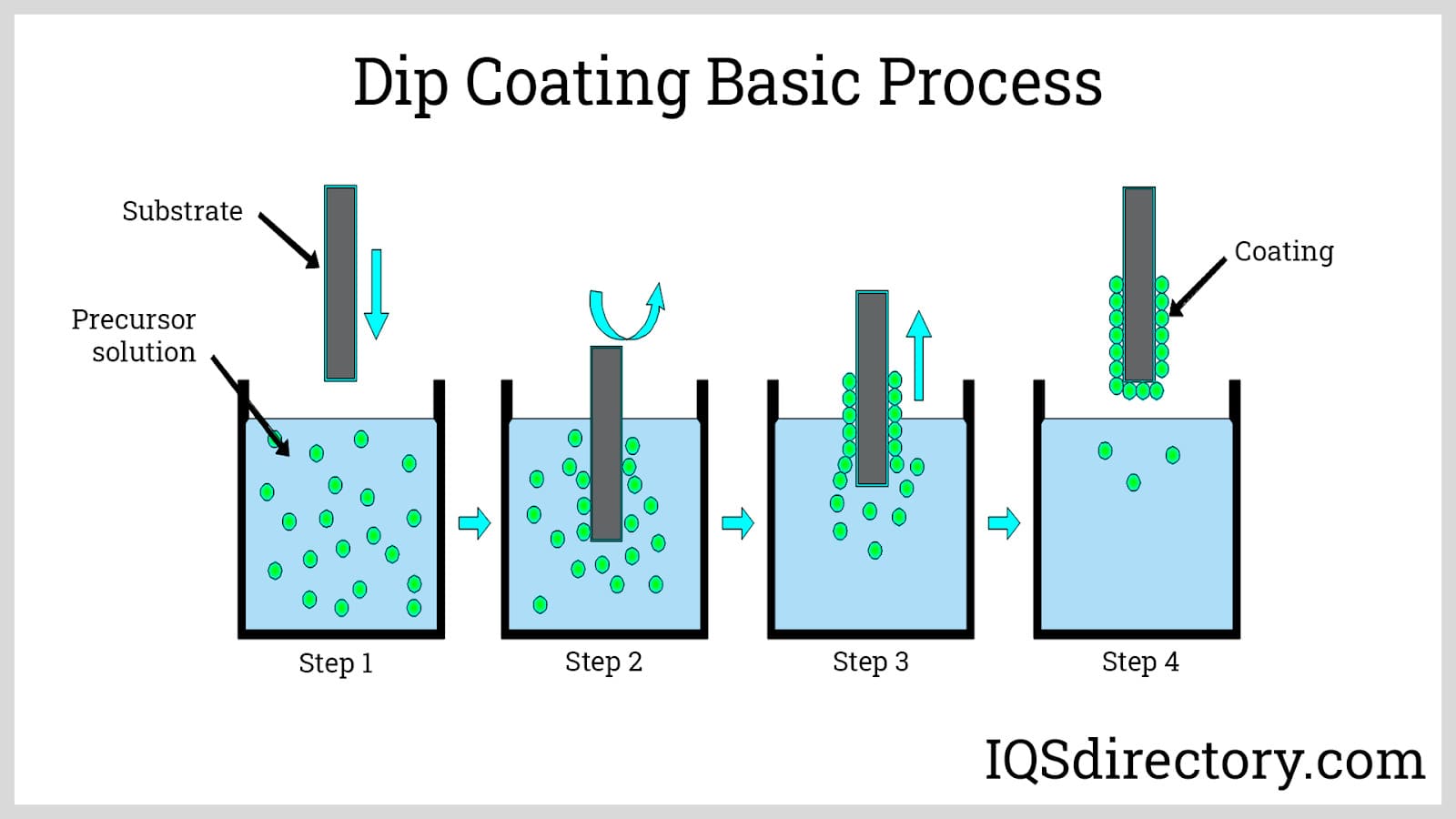
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding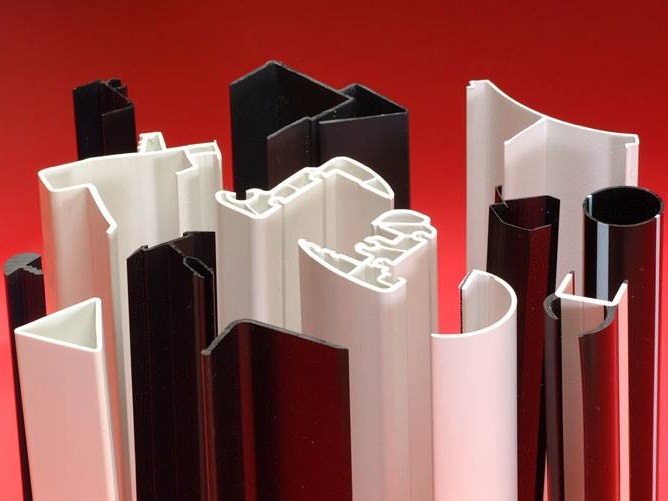 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotational Molding
Rotational Molding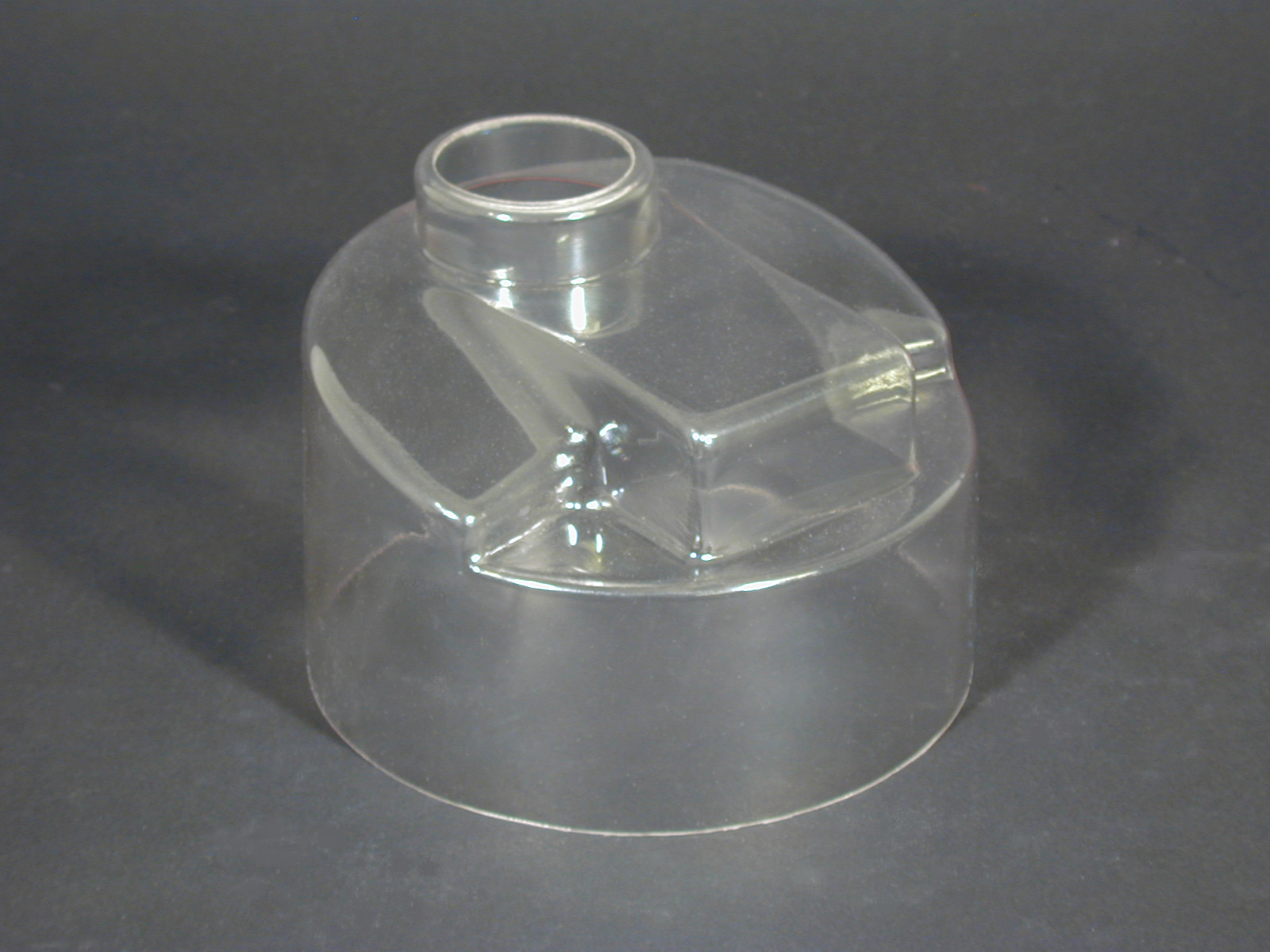 Vacuum Forming
Vacuum Forming Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services